What would it take for a new British left-wing party to succeed?
The Conversation
11 Jul 2025, 11:23 GMT+10
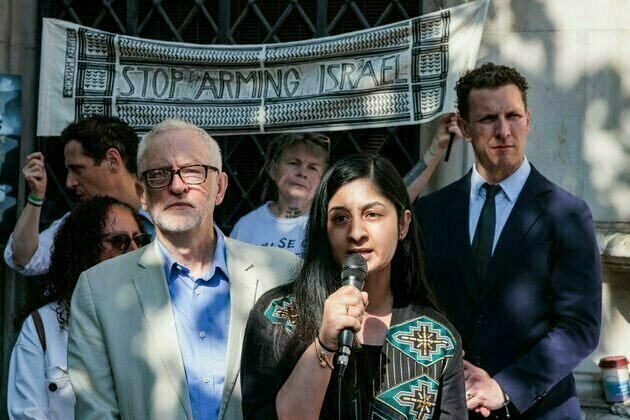

Last week, the MP for Coventry South, Zarah Sultana, made an audacious decision. Having already lost the Labour party whip for opposing the two-child benefit cap, Sultana announced she would co-lead a new left-wing party with Jeremy Corbyn, who was expelled from Labour in 2024.
From one angle, her decision may seem simple. Discontent with Keir Starmer's Labour government, on everything from welfare cuts to Gaza, has never been higher, and Sultana is a vocal critic. Yet, launching a (still unnamed) new party is bold. It tackles head-on an old and vexing question for socialist critics of capitalism in the UK.
In 1976, the socialist theorist Ralph Miliband (yes, Ed and David's dad) described the faith in Labour's capacity to become a socialist vehicle as "the most crippling of all illusions". But socialists who agree with Miliband senior then have an almighty problem.
Writing months after the 2019 defeat of Corbyn's Labour party, the veteran "New Left" academics Colin Leys and Leo Panitch echoed Miliband in their book Searching for Socialism. But they also saw few immediate alternatives with "any prospect of electoral success". This, they wrote, is the "central dilemma" for British democratic socialists.
Get your news from actual experts, straight to your inbox. Sign up to our daily newsletter to receive all The Conversation UK's latest coverage of news and research, from politics and business to the arts and sciences.
The reaction to Sultana's announcement from the British left has been accordingly mixed. Leaks revealed that Corbyn's team was caught off guard. Responses from prominent potential supporters were reserved. Momentum, the left-wing grassroots organisation, hastily distributed the pamphlet Why Socialists Should Be in the Labour Party.
It's too early to know whether these issues are teething problems or portents. But the barriers to Sultana's venture are formidable. What would it take for a new left-wing party to succeed? What would "success" even look like?
A careful reading of political history can help us answer these questions. This is not the first time that new parties have emerged from Labour factionalism. Many readers will be aware of the 1981 departure of the "gang of four" Labour figures, who founded the Social Democratic party (SDP) that later merged with the Liberal party to form the Liberal Democrats.
Nor is it the first time that smaller parties have appeared on Labour's left. Between 1920 and 1991, the Communist party of Great Britain was a potent force in the trade union movement. From the 1990s to the 2010s, several vehicles contested local and national elections against Labour, from the Socialist Alliance to Left Unity.
Each of these iterations had its historical peculiarities. But stepping back, we can identify three recurring challenges that any left-wing insurgent party must confront.
First, they must agree on an electoral strategy and purpose, given the institutional brutality of British democracy. The UK has some proportional elections, including in Scotland and Wales (expected to be next contested in 2026). Councils are also possible avenues of influence.
But there is no avoiding the fact that legislative and executive power is hoarded in the House of Commons, elected by first past the post. Labour will discourage possible defectors by warning that a split in the left vote will let in the right. Neil Kinnock, Labour's former leader who found himself fighting off the SDP while trying to evict Thatcher in the 1980s, dubbed Sultana and Corbyn's venture the "Farage assistance party".
Left of Labour parties are often aware of the risk. Indeed, far left activists have in the past advocated voting Labour, with "varying degrees of (un)enthusiasm".
Advocates of a new party will note that Labour is only polling in the low 20s, suggesting a pool of ex-Labour voters potentially interested in shopping around. However, there are others it could torpedo too.
One recent poll on support for a hypothetical Corbyn-led party - which we should take with some salt - found that its 10% support comes partly from eating into the Green vote. An electoral arrangement with the Greens, on the other hand, may require shared policy platforms, raising the question of why a separate party is needed.
A poll from More in Common conducted specifically about a Sultana-Corbyn party found 9% of Labour voters and 26% of current Green voters saying that would vote for such a party.
The Socialist Labour party (SLP) - founded in 1996 by the prominent trade unionist Arthur Scargill in reaction to Tony Blair's New Labour - is the obvious cautionary tale. Scargill wanted a purer, better Labour party. Yet, Labour looked set to kick out an 18-year-long Conservative government.
Scargill could not convince many sympathetic activists to join. As historian Alfie Steer argues, the SLP instead became dominated by socialists hostile to the Labour party. The party could not overcome the resultant contradictions in its purpose and collapsed into acrimony.
The SLP also illustrates the second key consideration: timing. The SLP struggled partly because it launched just as Labour was sweeping triumphantly into power. Sultana's timing is arguably more astute. She has waited for Starmer's bubble to burst and for disillusionment to fester.
However, the broad left within Labour has also just found its voice by rebelling against government policy. The temptation for a risk-averse Labour activist may be to leap onto this critical bandwagon without taking the more dangerous step of defecting.
Read more: The mistakes Keir Starmer made over disability cuts - and how he can avoid future embarrassment
The final challenge is securing institutional durability without debilitating splits. It is telling that Sultana felt compelled to include Corbyn's name despite his reported reservations.
Sultana herself has an impressive political profile, especially on TikTok. Any new party will rely heavily on prominent spokespeople to force it into the national conversation. Yet, such vehicles can become trapped by their dependence on individuals. The Respect party of the 2000s, for example, was reliant on the charismatic but polarising figure of George Galloway.
The fledgling party will also need a lasting structure that determines how candidates are selected and policy is formed. This risks dragging it into dreaded constitutional debates. It is already reportedly divided over the existence of co-leaders.
Intra-party democracy is off-putting to outsiders. But as constitutional scholar Meg Russell argues, it speaks to fundamental questions about the extent, and limits, of democracy. Such disputes have frequently wracked the left (and the radical right, as Reform's recent constitutional changes show).
To what extent should policy be "democratically" decided? Should a new party limit who can join, and if so, on what criteria? How will leaders be selected? From the CPGB to the SLP, these questions have proven divisive in the past. They could easily prove so again.
The new party faces severe challenges, but it would be unwise to write it off completely. In a volatile context, it has a chance to make its mark if it is clear in its strategic electoral purpose, cultivates an institutional and activist base and times its interventions astutely. But the obstacles to success are enormous - and with Reform currently polling top, the risks are high.
 Share
Share
 Tweet
Tweet
 Share
Share
 Flip
Flip
 Email
Email
Watch latest videos
Subscribe and Follow
Get a daily dose of Liverpool Star news through our daily email, its complimentary and keeps you fully up to date with world and business news as well.
News RELEASES
Publish news of your business, community or sports group, personnel appointments, major event and more by submitting a news release to Liverpool Star.
More InformationInternational
SectionGaza War sucking life out of an Israeli generation
In the past month alone, 23 Israeli soldiers have been killed in Gaza—three more than the number of remaining living hostages held...
Faulty IT system at heart of UK Post Office scandal, says report
LONDON, U.K.: At least 13 people are believed to have taken their own lives as a result of the U.K.'s Post Office scandal, in which...
Travelers can now keep shoes on at TSA checkpoints
WASHINGTON, D.C.: Travelers at U.S. airports will no longer need to remove their shoes during security screenings, Department of Homeland...
Rubio impersonator used AI to reach officials via Signal: cable
WASHINGTON, D.C.: An elaborate impersonation scheme involving artificial intelligence targeted senior U.S. and foreign officials in...
Warsaw responds to migration pressure with new border controls
SLUBICE, Poland: Poland reinstated border controls with Germany and Lithuania on July 7, following Germany's earlier reintroduction...
Deadly July 4 flash floods renew alarm over NWS staffing shortages
WASHINGTON, D.C.: After months of warnings from former federal officials and weather experts, the deadly flash floods that struck the...
UK
SectionFaulty IT system at heart of UK Post Office scandal, says report
LONDON, U.K.: At least 13 people are believed to have taken their own lives as a result of the U.K.'s Post Office scandal, in which...
Ex-UK PM Sunak takes advisory role at Goldman Sachs
NEW YORK CITY, New York: Former British prime minister Rishi Sunak will return to Goldman Sachs in an advisory role, the Wall Street...
Gold ETF inflows hit 5-year high as tariffs drive safe-haven bets
LONDON, U.K.: Physically backed gold exchange-traded funds recorded their most significant semi-annual inflow since the first half...
BP appoints ex-Shell finance chief Simon Henry to board
LONDON, U.K.: This week, BP appointed Simon Henry, former Shell finance chief, to its board as a non-executive director effective September...
Russia among 4 systemic risk countries for Italian banks
MILAN, Italy: Italian regulators have flagged four non-EU countries—including Russia—as carrying systemic financial risk for domestic...
Anupam Kher, Boman Irani arrive at Rashtrapati Bhavan to attend special screening of 'Tanvi The Great' with President Murmu
New Delhi [India], July 11 (ANI): Legendary actor Anupam Kher and Boman Irani arrived at Rastrapati Bhavan in Delhi to attend the special...